The Future of Healthcare: How Facial Expression Analysis is Revolutionizing Medical Monitoring
Healthcare technology has evolved dramatically over the past decade, moving from basic monitoring systems to sophisticated, AI-driven solutions that can detect the subtlest changes in human physiology. While traditional vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature remain cornerstone metrics, a new frontier has emerged that promises to revolutionize how we understand and monitor human health: facial expression analysis.
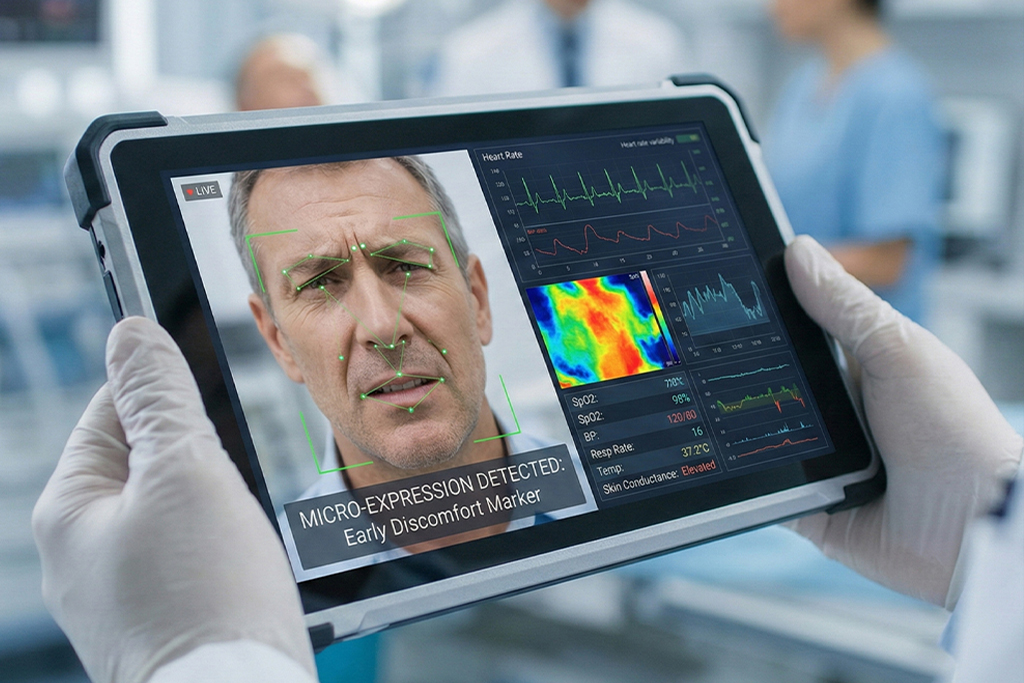
The vitalChair™ represents this next generation of medical monitoring technology, capable of measuring over 50 body vitals through advanced sensor integration and artificial intelligence. Among its most innovative features is its ability to analyze facial expressions—a capability that opens doors to unprecedented insights into patient health, comfort, and early disease detection.
But why facial expressions? The human face contains 43 muscles that work in complex combinations to create thousands of micro-expressions, many of which occur involuntarily in response to pain, discomfort, neurological changes, or emotional states. These expressions often precede verbal communication and can provide healthcare providers with critical information about a patient's condition before symptoms become apparent through traditional assessment methods.
The Science Behind Facial Expression Analysis in HealthcareUnderstanding the Facial Coding System
Facial expression analysis in medical applications builds upon decades of psychological and neurological research. The foundation lies in the understanding that facial expressions are not merely emotional displays—they are physiological responses that can indicate pain levels, cognitive function, neurological health, and overall patient wellbeing.
Every facial movement is controlled by specific muscle groups that contract and relax in measurable patterns. When these patterns deviate from normal baselines, they can indicate various medical conditions or changes in a patient's status. This biological fact forms the cornerstone of medical-grade facial expression monitoring systems.
Technology Behind InnovationModern facial expression analysis systems employ sophisticated artificial intelligence algorithms that can detect and interpret the smallest facial movements with remarkable precision. The process involves several critical components:
Facial Landmark Detection Advanced computer vision systems identify key anatomical points on the face, including the corners of the eyes, eyebrows, nose tip, mouth corners, and jawline. These landmarks serve as reference points for measuring facial movement and deformation. High-resolution cameras and specialized sensors can detect movements as small as 0.1 millimeters, allowing for incredibly precise monitoring of facial changes.
Feature Extraction and Analysis Once landmarks are established, the system analyzes how these points move and change over time. This includes measuring muscle contractions, skin deformation, changes in facial geometry, and temporal patterns of movement. Technology can distinguish between voluntary expressions (like smiling for a photo) and involuntary responses (like grimacing from pain).
Machine Learning Integration Sophisticated algorithms trained on extensive datasets learn to associate specific facial movement patterns with medical conditions, pain levels, and emotional states. These systems continuously improve their accuracy through exposure to diverse patient populations and validated medical outcomes.
Real-Time Data Processing Modern systems can process facial expression data in real-time, providing healthcare providers with immediate insights into patient status. This capability is particularly valuable in critical care settings where rapid changes in patient condition require immediate attention.
Medical Applications: Transforming Patient Care
Automated Pain AssessmentOne of the most significant applications of facial expression analysis in healthcare is automated pain assessment. Traditional pain evaluation relies heavily on patient self-reporting using subjective scales, which can be unreliable due to factors like patient communication difficulties, cultural differences, or cognitive impairment.
Facial expression analysis provides an objective, quantitative approach to pain measurement. Research has identified specific facial action units that correlate strongly with pain intensity, including brow lowering, eye closing, nose wrinkling, and lip corner depression. By monitoring these indicators continuously, healthcare providers can:
- Detect breakthrough pain in patients unable to communicate verbally
- Monitor pain relief effectiveness in real-time during treatment
- Identify pain patterns that may indicate complications or treatment needs
- Provide more accurate pain management for pediatric, elderly, or cognitively impaired patients
Facial expression analysis shows remarkable promise in detecting early signs of neurocognitive disorders and other medical conditions before conventional symptoms become apparent.
Neurocognitive Disorders Conditions like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and other forms of dementia often present with subtle facial expression changes months or years before cognitive symptoms become noticeable. These may include:
- Reduced facial expressiveness (hypomimia) in Parkinson's disease
- Changes in micro-expression timing and intensity in Alzheimer's
- Alterations in emotional expression recognition and production
- Asymmetrical facial movements that may indicate neurological changes
Genetic Conditions Certain genetic disorders present with characteristic facial features or expression patterns. Early detection through automated analysis can lead to faster diagnosis and intervention, particularly important in pediatric cases where early treatment can significantly impact long-term outcomes.
Mental Health Monitoring Depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions often manifest through changes in facial expressions, including reduced positive expressions, increased negative affect displays, and changes in expression timing and intensity. Continuous monitoring can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans and detect concerning changes early.
Patient Comfort and Treatment MonitoringBeyond disease detection, facial expression analysis provides valuable insights into patient comfort and treatment effectiveness. This application is particularly valuable in:
- Intensive Care Units: Monitoring sedated or intubated patients who cannot communicate verbally
- Surgical Recovery: Assessing post-operative pain and comfort levels
- Chronic Disease Management: Tracking daily comfort and quality of life metrics
- Rehabilitation Services: Monitoring patient motivation and engagement during therapy sessions
Technical Implementation and Accuracy Considerations
Sensor Technology and Data CollectionModern facial expression analysis systems integrate multiple sensor technologies to ensure accuracy and reliability:
High-Resolution Imaging Advanced camera systems capture detailed facial images at high frame rates, enabling detection of rapid micro-expressions and subtle changes in facial topology.
Infrared and Thermal Sensing These technologies can detect changes in blood flow and skin temperature that accompany facial expressions, providing additional data layers for more accurate analysis.
Multi-Spectral Analysis Some systems employ multiple light wavelengths to penetrate different skin layers, revealing physiological changes invisible to conventional cameras.
Algorithmic Approaches and ValidationThe accuracy of facial expression analysis systems depends heavily on the quality of their underlying algorithms and training data:
Deep Learning Models Convolutional neural networks and other deep learning architectures have shown remarkable success in facial expression recognition, often achieving accuracy rates above 95% in controlled environments.
Cross-Cultural Validation Ensuring system accuracy across diverse populations requires extensive training on varied demographic groups, accounting for cultural differences in expression patterns and anatomical variations.
Clinical Validation Studies Medical applications require rigorous clinical testing to validate accuracy against established medical assessments and ensure reliability in real-world healthcare environments.
Challenges and Considerations for Clinical Adoption
Data Privacy and SecurityThe implementation of facial expression analysis in healthcare settings raises significant privacy concerns that must be addressed through comprehensive security measures:
Patient Consent and Data Ownership
Clear protocols must establish patient consent procedures and data ownership rights, ensuring patients understand how their facial expression data will be used, stored, and shared.Encryption and Secure Storage Facial biometric data requires the highest levels of security, including end-to-end encryption, secure storage protocols, and limited access controls.
Regulatory Compliance Healthcare applications must comply with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and other relevant privacy laws, requiring careful attention to data handling and patient rights.
Accuracy and Clinical ReliabilityWhile facial expression analysis shows great promise, several factors can affect accuracy in clinical settings:
Individual Variations Factors like age, ethnicity, medical conditions affecting facial muscles, and individual expression patterns can influence system performance. Ongoing calibration and personalization features help address these challenges.
False Positive and Negative Rates Understanding system limitations and establishing appropriate thresholds for clinical decision-making is crucial for safe implementation.
Clinical Evidence Requirements Regulatory agencies require substantial clinical evidence demonstrating safety and efficacy before approving medical applications of new technologies.
Standardization Efforts Industry organizations are working to establish standards for facial expression analysis in healthcare, ensuring consistency and interoperability across different systems and vendors.
The Future Landscape: Emerging Trends and Innovations
Integration with Electronic Health RecordsThe future of facial expression analysis lies in seamless integration with existing healthcare infrastructure:
Real-Time EHR Updates Automated systems that update patient records with facial expression-derived insights, providing healthcare teams with comprehensive, real-time patient status information.
Predictive Analytics Combining facial expression data with other health metrics to create predictive models for patient deterioration, treatment response, and health outcomes.
Informed Consent and Patient AutonomyHealthcare providers implementing facial expression analysis must ensure patients fully understand the technology and its implications:
Transparent Communication Patients should receive clear explanations of how the technology works, what data is collected, and how it will be used in their care.
Conclusion: A New Era in Patient-Centered HealthcareThe integration of facial expression analysis into medical monitoring represents a significant leap forward in patient-centered healthcare. Technologies like those embedded in the vitalsChair™ demonstrate how sophisticated AI and sensor systems can provide healthcare providers with unprecedented insights into patient wellbeing, comfort, and health status.
As we look toward the future, the potential applications continue to expand. From early detection of neurocognitive disorders to real-time pain management optimization, facial expression analysis offers the promise of more responsive, personalized healthcare that can detect problems before they become critical and ensure patient comfort throughout the care journey.
However, realizing this potential requires careful attention to the challenges of privacy, accuracy, and ethical implementation. Success will depend on collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, regulatory agencies, and patients themselves to create systems that are not only technically sophisticated but also trustworthy, equitable, and truly beneficial to patient care.
The healthcare industry stands at the threshold of a new era where technology can read the subtle language of the human face to provide better, more compassionate care. As these systems continue to evolve and mature, they promise to transform not just how we monitor health, but how we understand and respond to human suffering and wellbeing in all its forms.
The future of healthcare is not just about collecting more data about understanding the human experience more deeply and responding with greater precision, empathy, and effectiveness. Facial expression analysis represents a crucial step toward that future, offering a window into the patient experience that has never been available to medical science.